Calculation of Work Done in Various Thermodynamic Processes
Calculation of Work Done in Various Thermodynamic Processes: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Work Done in Reversible Adiabatic Process, Graph of Isochoric Process, Reversible Adiabatic Vs Reversible Isothermal for Ideal Gases & Reversible Adiabatic Vs Irreversible Adiabatic for Ideal Gases etc.
Important Questions on Calculation of Work Done in Various Thermodynamic Processes
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, its
Absolute zero is defined as the temperature
moles of an ideal gas expands isothermally against a constant pressure of Pascal from L.The amount of work involved is
Two moles of gas are initially at temp and occupy a volume of litres. The gas is first expanded at constant pressure until its volume is doubled. Then it undergoes reversible adiabatic change, until the volume become , then predict the value of (where is the final temperature, )
The magnitude of reversible work done by an ideal gas in four different processes: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, constant pressure expansion, and free expansion are , and respectively. Choose the right order of sequence for the magnitude of the work done. (Change in the volume is same for all the processes.)
An ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion at constant pressure. During the process:
A gas absorbs 58.63 joules of heat, when the gas expands from 2 litre at STP to 2.5 litre at 1 atm. Calculate the Change in its internal energy in joules is
(Round off the answer up to three significant figures)
and for the following process for a monoatomic gas are:
Consider the reversible isothermal expansion of an ideal gas in a closed system at two different temperatures and The correct graphical depiction of the dependence of work done on the final volume
Five moles of an ideal gas at is expanded isothermally from an initial pressure of to against at constant external . The heat transferred in this process in is (Rounded-off of the nearest integer) [Use ]
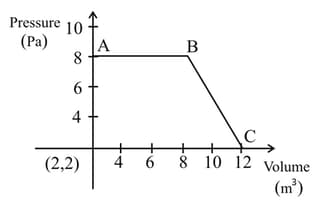
The magnitude of word done by a gas that undergoes a reversible expansion along the path ABC shown in the figure is___________Nm.
During the free expansion of an ideal gas in an isolated chamber,
of an ideal gas at expands isothermally and reversibly from a volume of to . The work done (in by the gas is
Identify the incorrect statement-
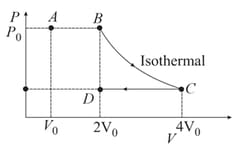
The process in which an ideal gas undergoes change from to as shown in following diagram is:
A certain quantity of an ideal gas is expanded from to isothermally in three steps. The pressure of these three states are and respectively. Now, the gas is brought back to the initial state by the given three steps again. Calculate the total work done on the system during this cycle in . (Take : )
An ideal gas is taken around the cycle as
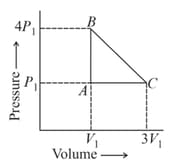
The work done in the cyclic process is:
oxygen gas expands at , to occupy double of its original volume. The work done during the process is:
For an isothermal process for an ideal gas, is equal to:
For an ideal gas equals to:
